How DNS Works
Learn how DNS works in 2 minutes

Post by Sanjay Bhandari - Published at 2/4/2023
Domain Name System (DNS) was introduced to bridge the communication gap between humans and computers. DNS resolves names to numbers, in straight human-friendly domain names to computer-friendly IP addresses.
First, let’s start with a basic understanding of what DNS is. DNS stands for Domain Name System and is essentially the internet’s phonebook. DNS matches human-friendly domain names (like www.mypage.com) to the IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the internet.
When you type a URL into your browser, the first thing your computer does is check its local host file. The host file is a simple text file that maps domain names to IP addresses. This allows your computer to quickly look up the IP address of a website without having to send a request to a DNS server. If the website you are trying to access is not in the host file, your computer will then check its local cache. This is a small storage area on your computer where recently looked-up website addresses are stored.
Your computer will check the operating system cache if the website is not in the local cache. This is a storage area shared by all applications on your computer where recently looked-up website addresses are stored. If the website is still not found, your computer will check the cache on your router. This is a small storage area on your router where recently looked-up website addresses are stored. If the domain name isn’t in the host file or cache, your computer will send a request to a DNS server. This request is called a DNS query. The DNS server will then search its database of the domain names to IP address mappings and return the correct IP address to your computer.
Once your computer receives the IP address from the DNS server, it will use that address to connect to the website. From that point on, your computer will store the domain name and IP address in its DNS cache so that it can quickly look up that information the next time you visit the website.
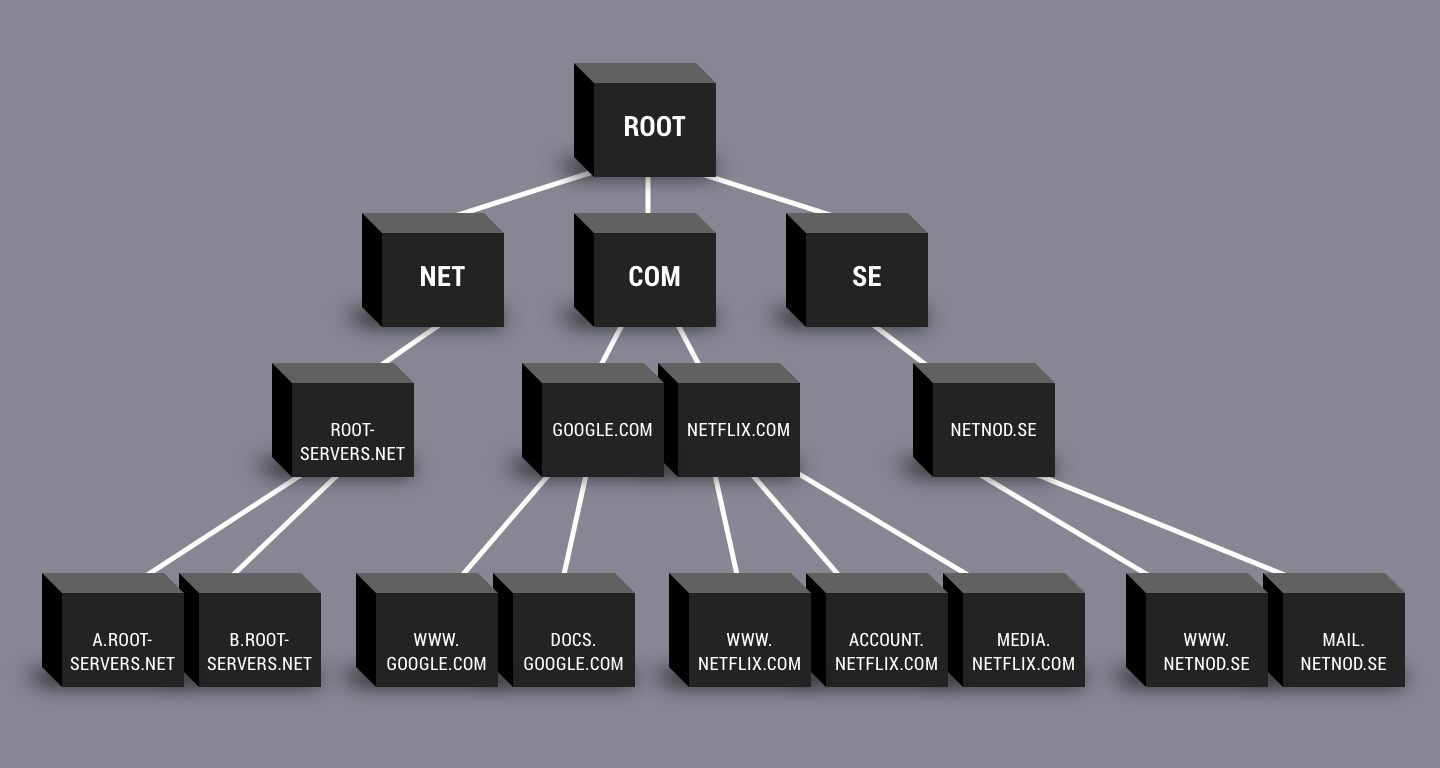
Lastly, it is worth noting that DNS is a hierarchical system, which means that DNS servers are arranged in a tree-like structure. This structure is called the DNS namespace.
The root of the namespace is the root DNS server, which is responsible for directing traffic to the appropriate DNS server for the specific domain name being requested. This allows for efficient and quick resolution of domain names to IP addresses, allowing the internet to function smoothly.
Domain Name System is one of the important aspects of the internet. It is the first step in making the connection to the internet. It ensures the internet is not only user-friendly but also helps in loading the requested content efficiently. Without DNS, it would be a heavy burden for all of us, while we are living in the internet world with countless websites.
